Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) has revolutionized the way we approach prenatal care, offering a safe and highly accurate method to screen for potential genetic disorders in a developing fetus. As technology continues to advance, NIPT has become a game-changer for expecting parents, providing early insights into their baby’s health without the risks associated with more invasive tests.
What is NIPT?
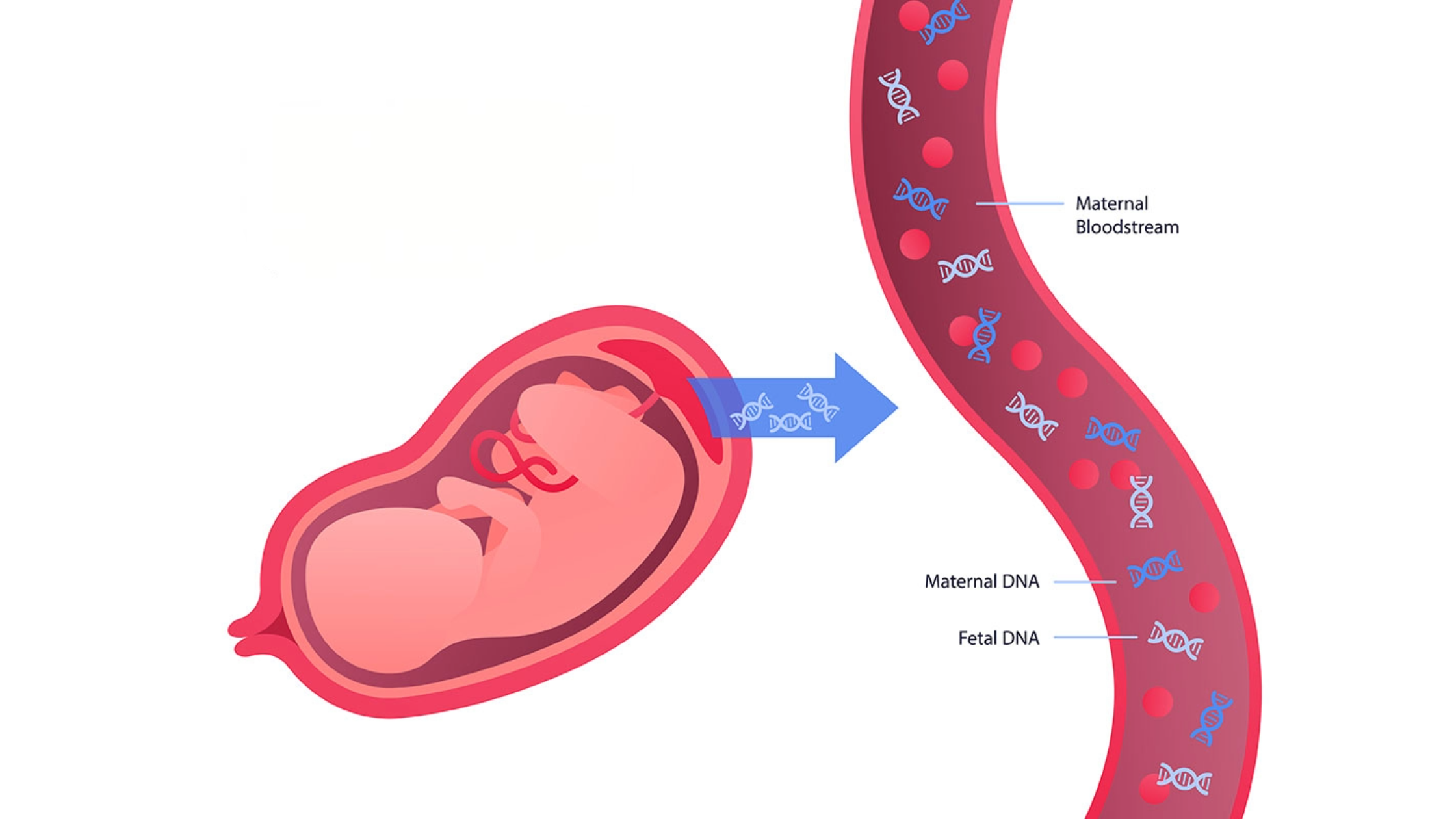
NIPT is a blood test that analyzes small fragments of fetal DNA (cfDNA) that circulate in the mother’s blood. This test is typically offered to pregnant women as a way to screen for certain genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13, and other chromosomal abnormalities. It can be performed as early as the 10th week of pregnancy and is considered one of the safest and most accurate screening methods available today.
How Does NIPT Work?
During pregnancy, both the mother’s and the fetus’s DNA can be found in the bloodstream. NIPT specifically isolates and analyzes the fetal DNA, searching for signs of chromosomal conditions. The test can detect the likelihood that the baby has specific genetic disorders based on the amount of cfDNA from each chromosome.
Unlike traditional screening methods, which rely on ultrasound and maternal blood markers to assess the risk of genetic conditions, NIPT uses a direct approach to assess fetal DNA, making it far more accurate and reliable.
Benefits of NIPT
- Non-invasive: Unlike other tests such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), NIPT poses no risk of miscarriage or harm to the baby. Since it only requires a simple blood draw from the mother, it is considered a safer option for both mother and baby.
- Early Detection: NIPT can be performed as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy, which allows for early detection of certain genetic conditions. Early detection can provide expectant parents with more time to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy.
- High Accuracy: NIPT is known for its high sensitivity and specificity, with accuracy rates often exceeding 99% for detecting conditions like Down syndrome. This makes it more reliable than traditional screening methods.
- Comprehensive Testing: While NIPT is often associated with Down syndrome, it can also screen for other conditions, including Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13, and even sex chromosome disorders like Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and others.
- Peace of Mind: For many expectant parents, NIPT offers peace of mind, knowing that the test can provide crucial information about the health of their baby early on, without the risks associated with invasive testing.
Limitations of NIPT
While NIPT is a powerful tool, it’s important to understand its limitations:
- Screening vs. Diagnostic: NIPT is a screening test, not a diagnostic test. This means it can only assess the likelihood of a condition, not provide a definitive diagnosis. A positive result from NIPT is often followed by additional diagnostic testing (such as amniocentesis or CVS) to confirm the result.
- False Positives/Negatives: Though rare, false positives and false negatives can occur. This is why it’s important to follow up with further diagnostic testing if NIPT indicates a potential issue.
- Limited Scope: NIPT primarily screens for certain chromosomal conditions. While it is highly accurate for these conditions, it does not detect all possible genetic disorders, birth defects, or health concerns that might affect a baby.
NIPT vs. Other Prenatal Screening Tests
NIPT is often compared to traditional prenatal screening methods, such as the first-trimester combined screening (which includes an ultrasound and blood tests to assess the risk of Down syndrome) and second-trimester maternal serum screening.
- Accuracy: NIPT has a much higher accuracy rate compared to these traditional screening methods. For instance, the combined screening test has a detection rate of around 85% for Down syndrome, while NIPT can detect over 99% of cases.
- Invasiveness: Traditional tests like amniocentesis and CVS involve collecting tissue samples from the placenta or amniotic fluid, which carries a small risk of miscarriage. NIPT, on the other hand, is non-invasive and carries no such risk.
- Early Testing: While traditional screening tests can often be done in the first trimester, they usually cannot offer the level of precision and early results that NIPT can.
The Future of NIPT
As research into NIPT continues to evolve, the potential for more comprehensive genetic screening in the future is immense. The scope of conditions that NIPT can detect is expanding, and the accuracy of the test is likely to improve even further. Moreover, the accessibility of NIPT is expected to increase, making it available to more pregnant women around the world.
Additionally, there are discussions about whether NIPT could eventually become a standard part of prenatal care, offered to all pregnant women as part of routine screening, much like other prenatal tests.